Understanding Jean Piaget's Developmental Theory: A Journey Through Cognitive Growth
Jean Piaget's developmental theory has significantly influenced our understanding of how children learn and develop cognitive skills over time. His insights have paved the way for educators and psychologists to create more effective teaching strategies that align with children's natural learning processes. By studying the stages of cognitive development, Piaget's work has helped us comprehend the complexities of how children perceive and interpret the world around them.
Through rigorous observation and research, Piaget identified stages of development that every child goes through, providing a framework that continues to be relevant in contemporary educational practices. This article delves into the intricacies of Piaget's developmental theory, exploring its key components, implications for education, and how it shapes our understanding of child psychology.
As we navigate through this exploration, we will answer critical questions about Piaget's contributions to developmental psychology and how his theories apply to various educational contexts. Join us on this enlightening journey to discover the depth of Jean Piaget's insights into cognitive development.
Who Was Jean Piaget?
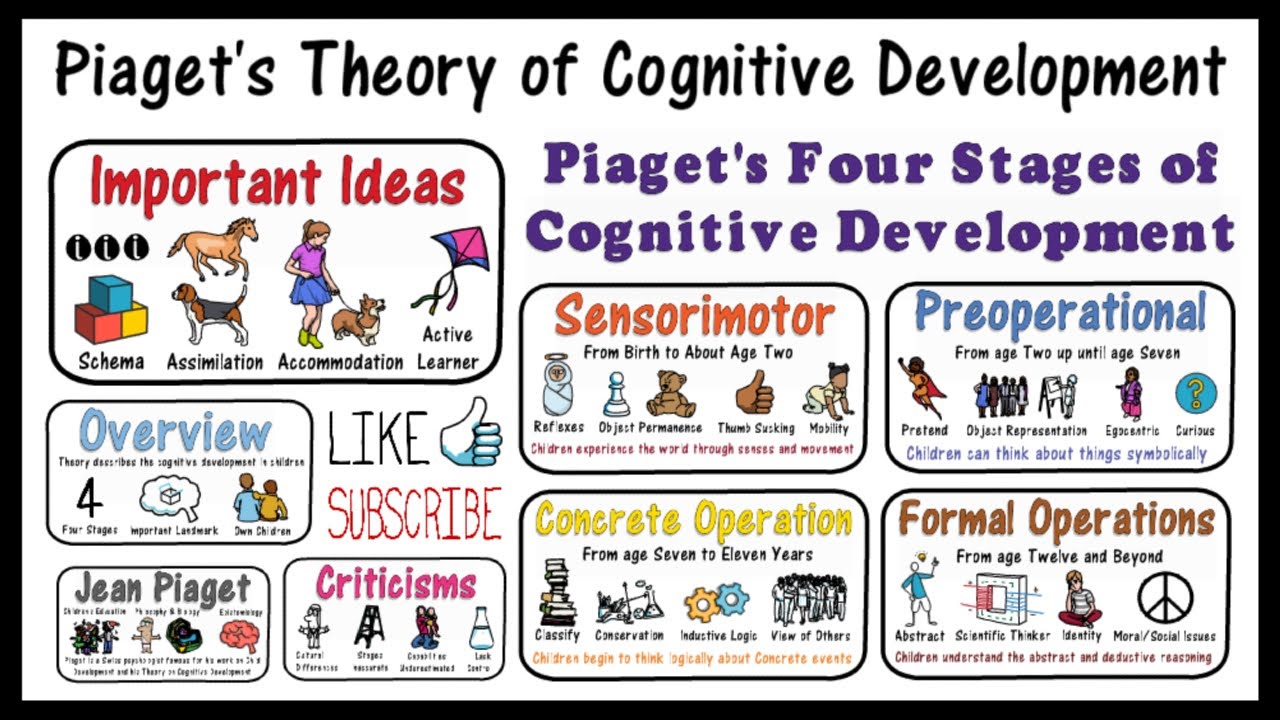
Jean Piaget was a Swiss psychologist and philosopher, renowned for his pioneering work in developmental psychology. Born on August 9, 1896, in Neuchâtel, Switzerland, Piaget displayed an early fascination with nature and the sciences. He later earned a degree in natural sciences from the University of Neuchâtel. His academic journey led him to study psychology, philosophy, and the field of child development, culminating in groundbreaking theories that would change the landscape of education and psychology.
What Are the Key Stages of Piaget's Developmental Theory?
Piaget's developmental theory is divided into four critical stages, each characterized by distinct cognitive abilities and ways of thinking. These stages are:
- Sensorimotor Stage (0-2 years): During this stage, infants learn about the world through their senses and motor actions. Object permanence develops, allowing children to understand that objects exist even when out of sight.
- Preoperational Stage (2-7 years): In this stage, children begin to engage in symbolic play and learn to manipulate symbols, but they lack the ability to perform operations mentally. They are egocentric and struggle with understanding others' perspectives.
- Concrete Operational Stage (7-11 years): Children start to think logically about concrete events, understand the concept of conservation, and can classify objects. They begin to grasp the idea of reversibility in operations.
- Formal Operational Stage (12 years and up): This stage marks the development of abstract reasoning and logical thinking. Adolescents can now think about hypothetical situations and use deductive reasoning.
How Does Piaget’s Theory Apply to Education?
The implications of Jean Piaget's developmental theory for education are profound. Understanding the cognitive abilities associated with each developmental stage allows educators to tailor their teaching methods to suit the learning needs of their students. Here are some key applications:
- Encouraging hands-on learning experiences during the sensorimotor stage.
- Utilizing storytelling and role-play to enhance symbolic thinking in preschoolers.
- Promoting problem-solving tasks that require logical thinking during the concrete operational stage.
- Facilitating discussions that encourage abstract reasoning and critical thinking in teenagers.
What Are the Criticisms of Piaget's Developmental Theory?
While Piaget's contributions to developmental psychology are widely recognized, his theories have faced criticism over the years. Some scholars argue that:
- Piaget underestimated the cognitive abilities of children, particularly in the preoperational stage.
- The stages of development may not be as rigid and universal as he proposed, as cultural and social factors can influence cognitive development.
- His research primarily focused on Western children, raising questions about the applicability of his theory across different cultures.
How Has Piaget's Work Influenced Modern Psychology?
Jean Piaget's developmental theory has had a lasting impact on various fields, including education, psychology, and child development. His work laid the foundation for subsequent theories, such as Vygotsky's socio-cultural theory, which emphasizes the role of social interaction in cognitive development. Furthermore, Piaget's methods of observation and analysis have influenced how researchers study children's cognitive processes today.
What Can We Learn from Jean Piaget's Developmental Theory?
The essence of Jean Piaget's developmental theory lies in its emphasis on the active role of learners in constructing their understanding of the world. It encourages educators and parents to:
- Recognize and respect the unique cognitive processes of each child.
- Provide appropriate challenges that stimulate cognitive growth.
- Foster an environment that encourages exploration, curiosity, and critical thinking.
Conclusion: The Legacy of Jean Piaget
In summary, Jean Piaget's developmental theory continues to be a cornerstone in our understanding of cognitive development. His systematic approach to studying children's thinking processes has provided invaluable insights that educators and psychologists still apply today. By recognizing the stages of cognitive development, we can create more effective learning environments that cater to the needs of children at various ages.
As we reflect on Piaget's contributions, it is clear that his legacy transcends time and culture, reminding us of the importance of fostering a love for learning and an understanding of the cognitive processes that shape our youth.
| Biography Details | Information |
|---|---|
| Name | Jean Piaget |
| Born | August 9, 1896 |
| Birthplace | Neuchâtel, Switzerland |
| Field | Psychology, Philosophy |
| Known For | Cognitive Development Theory |
| Died | September 16, 1980 |
Unveiling The Enigma Of Griselda Blanco Man
Unveiling The Brilliance: A Comprehensive Look At Messi's Career Stats
Unraveling The Mysteries: How Did Jeffrey Epstein Shape His Infamous Legacy?